GPS over multi-mode fibre link system
Utilise low-cost and readily-available multi-mode fibre to extend the distance between outdoor antenna and GPS repeater/receiver up to 1500 meters.

Multi-mode fibre optic cables – background
Multi-mode fibre (MMF) is a type of optical fibre mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus.
MMF is commonly used to support data traffic such as TCP/IP. It can be used to inter-connect switches and routers within the data infrastructure, and is sometimes used as a secure direct connection to desktop devices.
This cost-effective infrastructure can also be used to transport GNSS/GPS signals across distances up to 1500 meters from the antenna.
Why are GNSS/GPS signals needed inside a building?
There are two main reasons for wanting a GNSS/GPS signal inside a building.
- In addition to longitude, latitude, and altitude, GNSS/GPS signals provide a fourth dimension – time. Each satellite contains multiple atomic clocks, which contribute very precise time data to the GPS signals.
The timing element of a GNSS/GPS signal is used to synchronise data networks to the highly accurate atomic clocks. Applications include financial markets, power generating companies and industrial control systems, as well as fixed-line and cellular communications networks. - GNSS/GPS repeaters are used to provide signal in areas where it is not normally present.
A large building with laboratories, workshops and classrooms, for example, may use GPS signals to allow operation and testing of systems, without the need to go outside the building to achieve a GPS lock.
A GPS over fibre system allows the distribution of signal into spaces where coaxial cable may be impractical or unavailable.
Teleplan Forsberg RVL-1 link system for extending GNSS/GPS signals over multi-mode fibre.
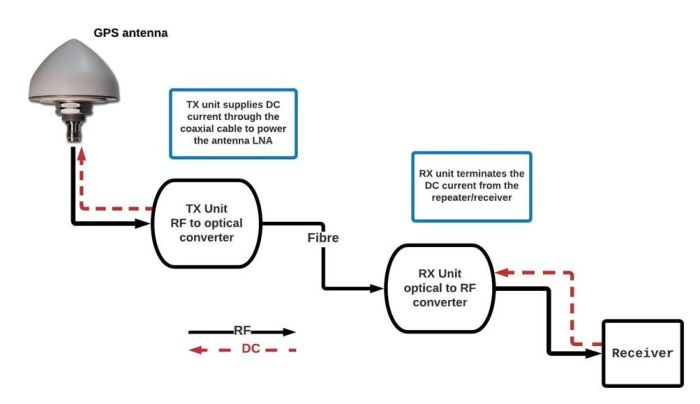
FalTech recommends the Teleplan Forsberg RVL-1 link system for extending GNSS/GPS signals over multi-mode mode fibre.
The weatherproof TX unit is mains-powered and can be mounted indoors or outdoors. It is designed to withstand extremes of temperature and adverse weather conditions.
The TX unit is placed near to the outdoor receiving antenna, and converts the RF signals into light by modulating a laser light source. The modulated light is then transported through an optical fibre to the optical receiver (RX) unit.
At the other end of the fibre optic link, the RX unit converts the light signal back into its original RF form, then amplifies and impedance matches it to the attached GPS receiver/repeater.
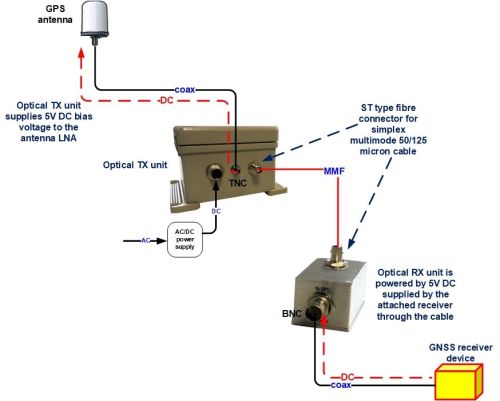
System operation
When the antenna and cable are intact and correctly installed, the TX unit will sense current draw through the low noise amplifier (LNA) in the antenna and will switch on the laser light source to the fibre.
The RX device receives light signals from the TX via the fibre. The RX unit LED shows green.
If the antenna or feeder cable are broken, or disconnected, the TX unit senses that no current is being drawn by the LNA and turns off the laser light source. The RX unit LED shows red.
The sensing circuit is a protection function of the RVL-1 , that prolongs the laser life by switching it off when there is no antenna connected.
RVL-1 GPS-over-fibre example applicatoin
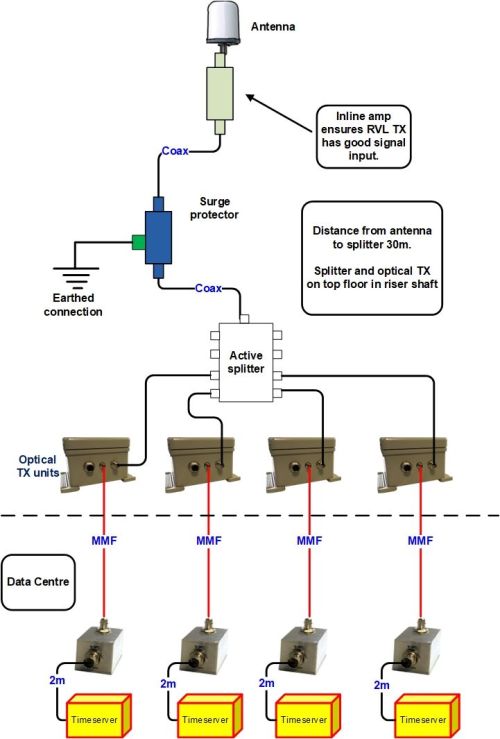
RVL-1 system providing GNSS/GPS timing signals in a datacentre
- The outdoor antenna receives a 5V bias voltage through the coaxial cable from the active splitter.
- The surge protector provides protection for the equipment “downstream in case of a lightning strike.
- The active splitter is lossless, and passes incoming signal to up-to 8 outputs.
- The TX units convert RF signal to light and launches it down the fibre optical link cables to the RX units.
- The RX units convert the optical data back to RF and outputs the GPS stream to the attached PNT servers.
Benefits of fibre optic cable
- Increased range when compared to coaxial cable systems – up to 1,500 metres on multi-mode fibre, and 10Km over single-mode fibre
- Optical fibre is a non-conducting dielectric glass media, is immune to strong electromagnetic fields and can be installed near high-voltage cables
- Signals suffer minimal degradation or delay
- Optical fibres can be routed safely through explosive or flammable atmospheres, for example, in petrochemical industries or munitions sites, without risk of ignition
- With the appropriate conversion devices, optical fibres can carry a huge range of RF signals with much less energy than copper cable and with significantly higher bandwidth
- Compared to thick, low-loss coaxial cable it is small, lightweight, easier to install and is durable
- The cost of a 200m single-mode fibre link is lower than the equivalent length of coaxial cable and amplifiers
There are many ways in which GPS over fibre can be used, aside from the application example shown above.
For more information, or to request a quote, select the Contact button below.
GPS signals can be transported over much larger distances via single-mode fibre.
Need help to decide which system is right for you?
Or call us on
